Cells are the basic unite of all life forms. They make up all living things. |
||||
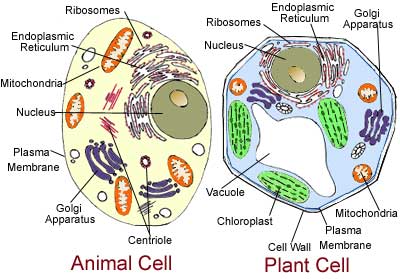 Plant Cells vs Animal Cells Plant Cells: - Have cell walls - Cloroplasts - Large central vacuole Animal Cells: - Do not have cell walls - Lysomes - Centrioles - Vacuole Both: - Cell membrane - DNA - Nucleus (contains DNA) - Mitochondria - Cytoplasm - Ribosomes (free/attached) - Gogi apparatus - Rough endoplasmic reticulum - Vesicle - Cytoskeleton Cell Speciallization and Organization: Cell Speziallization- different cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to do certain things in the organism. An example is the cells in a human's trachea which have cilia at the top of their serface that act like street sweepers that catch mucus, debris,and bacteria from getting into your lungs. Cell Organization- when special cells, like a muscle cell, are organized into tissue, like muscle tissue, then into organs, like the stomach, and lastly into organ systems, like the digestive system. Basically, cells make up tissue, tissue make up organs, and organs work together to make organ systems.
 |
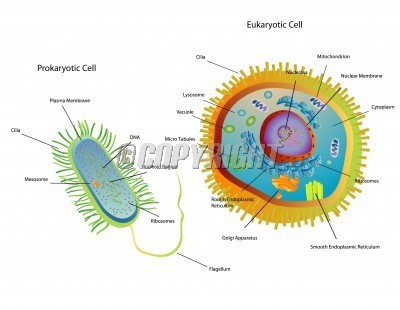 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Prokaryotes: - No nucleus - All unicellular - Smaller - Simple - Includes bacteria and archaea Eukaryotes: - Nucleus - Mostly multi-cellular - Larger (10-100x) - Complex - Includes plants, animals, fungi, and protists Both: - DNA - Cell membrane Endosymbiotic Theory: The endosymbotic theory is the explaination of mitichondria and chloroplasts and their double-membranes. Basically, it is when a cell recieves entry to an other cell without passing through it's cell membrane. The cells' membranes fuse together and locks the foreign material inside and as a result, an intracellular vesicle is formed. 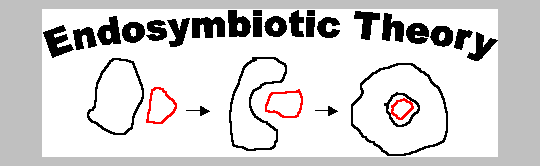 Emerging Diseases: Emerging diseases are unknown diseases that show up in a population for the first time or a well-known disease that has evolved and bacame harder to control. Emergine diseases can be very life-threatening to humans because they have little to no resistance to them and the populations haven't developed control methods yet. 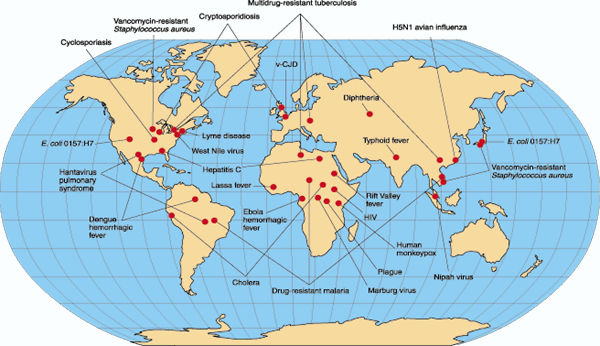 |
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells: Nucleus- contains DNA Vacuoles & vesicles- Store materials Lysosomes- break down and recycle macromolecules Cytoskeleton- maintain cell shape; moves parts of cell; helps cell membrane Centrioles- Organize cell division Ribosomes- synthesize proteines Endoplasmic reticulum- assembles protiens and lipids Golgi apparatus- modifies,sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for storage or transportation out of the cell Chloroplasts- convert solar energy to chemical energy stored in food Mitochondria- convert chemical energy in food to usable compounds Cell wall- shapes, supports, and protects the cell Cell membrane- regulates what enters and leaves the cell; protects and supports cell Organells Specially Involved in Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes- where proteins are assembled. Produce proteins by following coded information from the DNA. Endoplasmic reticulum- the rough ER is the portion of the ER that is involved in protein synthesis. The newly-made protiens leave the ribosomes and get inserted into the rough ER and are chemically modified. Golgi apparatus- modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other material from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell. The finishing touches are done to the proteins here before they are sent off to their final destination either inside or outside of the cell. Macromolecules: Lipids- store energy Carbs- main source of energy for living things (plants and some animals use carbs for structural purposes) Nucleic acids- store and transmit hereditary information Proteins- control rate of ractions and regulate cell processes |
||